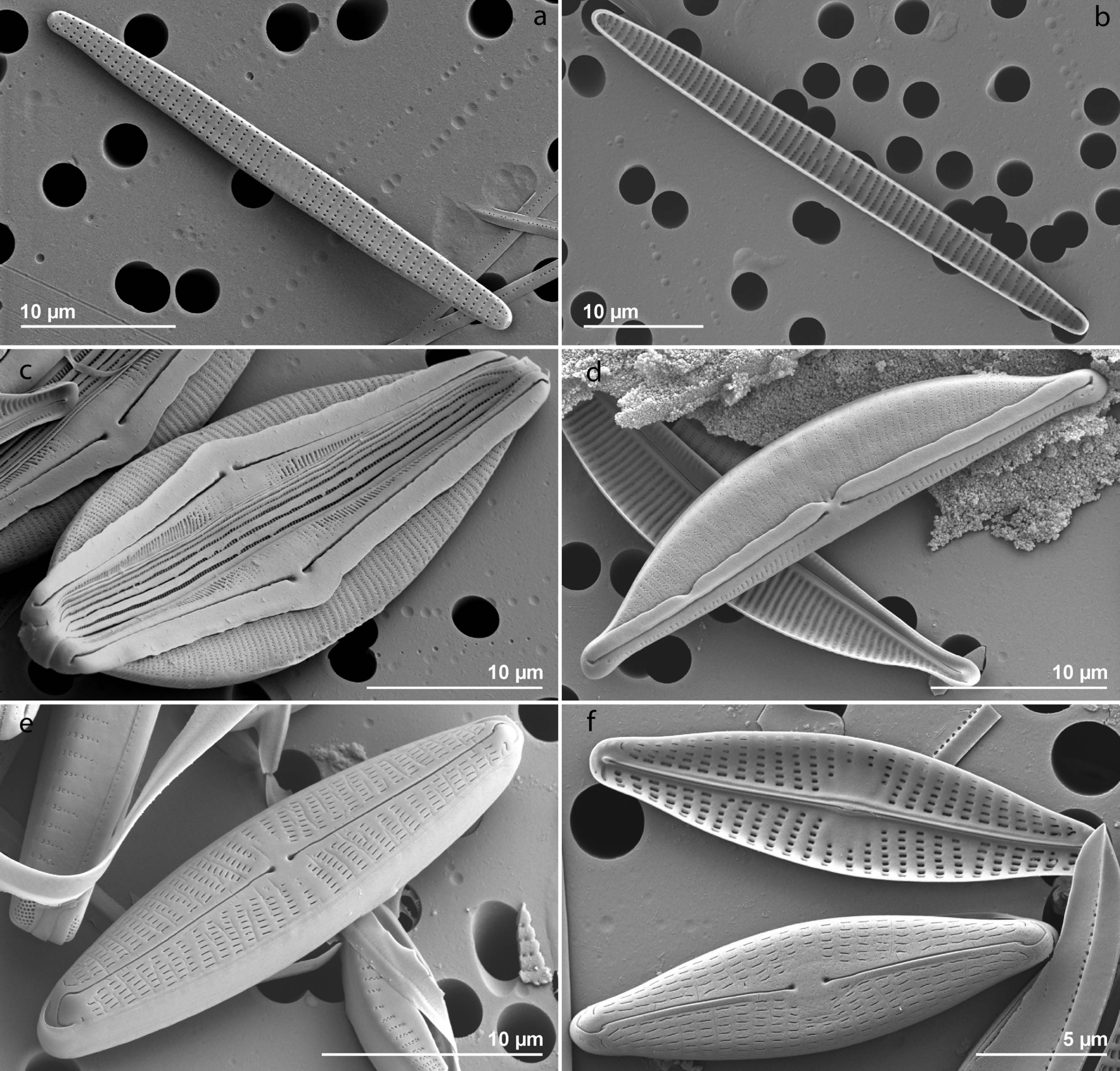
Un premier article de synthèse sur l’étude de la biodiversité des sources minérales a été écrit. Un focus a été donné sur les sources salées du Massif central. Ainsi, parmi les sources étudiées, les communautés de diatomées de 79 sources ont été analysées et les variables physico-chimiques examinées afin d’identifier celles structurant les peuplements.
Navicula sanctamargaritae est associée aux fortes concentrations en potassium tandis que Halamphora coffeaformis est associées au fortes concentrations en lithium, sodium, potassium chlorure, brome et aux valeurs élevées de TDS, conductivité et pH.
A first review article on the study of the biodiversity of mineral springs has been written. A focus was given on the saline springs of the Massif Central. Thus, among the springs studied, the diatom communities of 79 springs were analyzed and the physico-chemical variables examined in order to identify those structuring the communities.
Navicula sanctamargaritae is associated with high concentrations of potassium while Halamphora coffeaformis is associated with high concentrations of lithium, sodium, potassium chloride, bromine and high values of TDS, conductivity and pH.
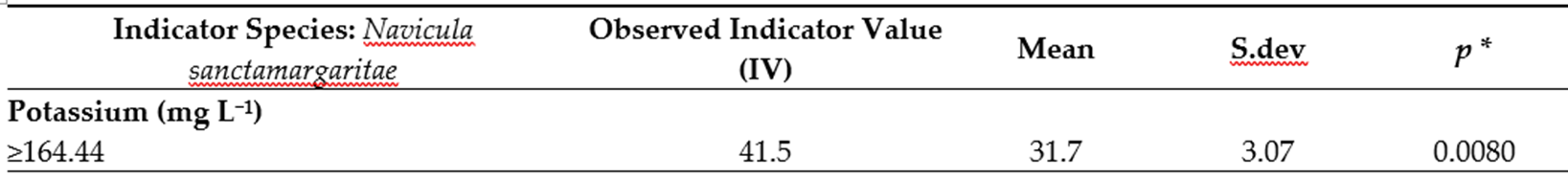
greater than 20%, along with mean standard deviation and significant p-values (* < 0.05): Navicula sanctamargaritae. Different
diatoms were linked to each group.
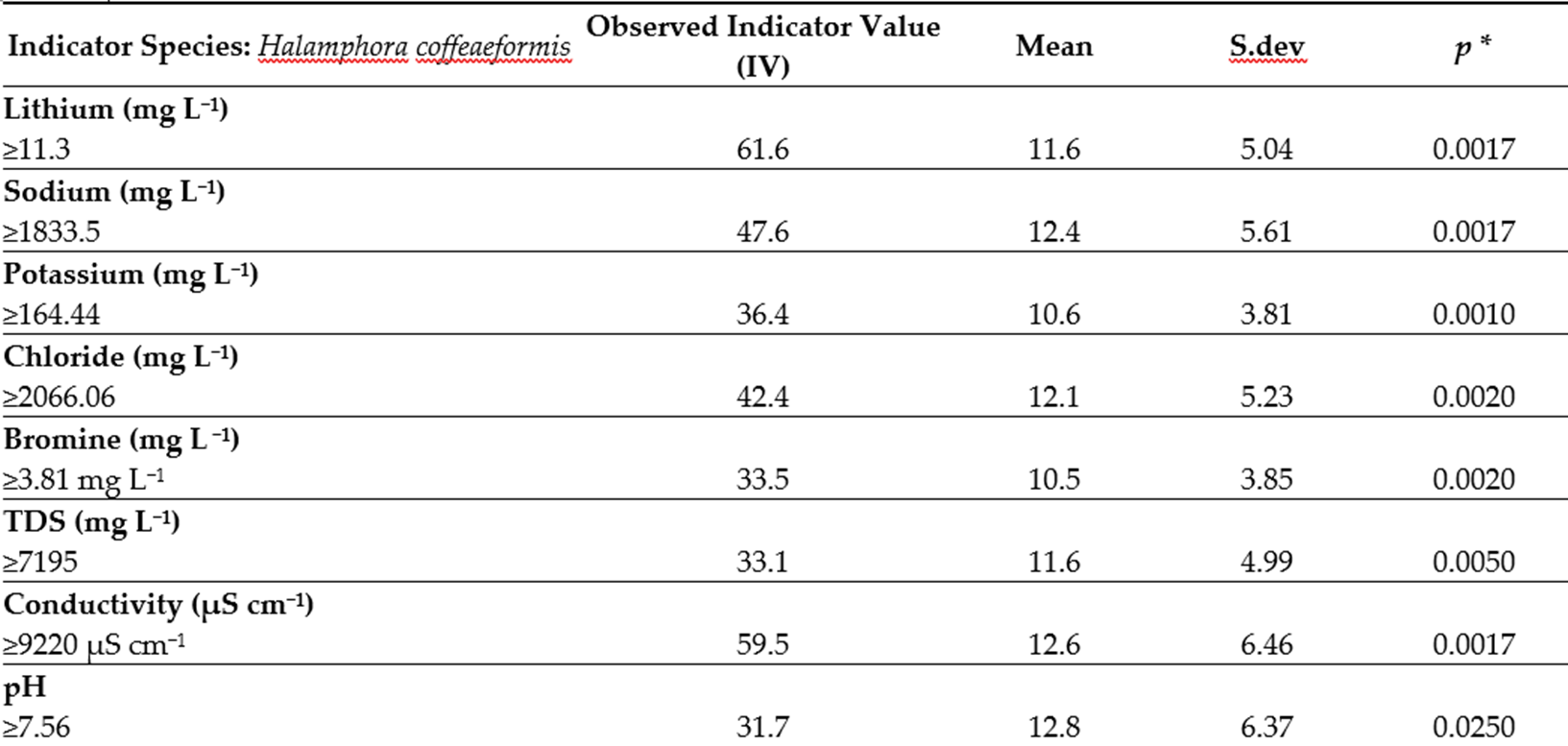
greater than 20%, along with mean standard deviation and significant p-values (* < 0.05): Halamphora coffeaformis. Different
diatoms were linked to each group.
Pour lire l’article: